Corporate Governance
Corporate Governance Guidelines
(Revised:February 12, 2025)(316KB)
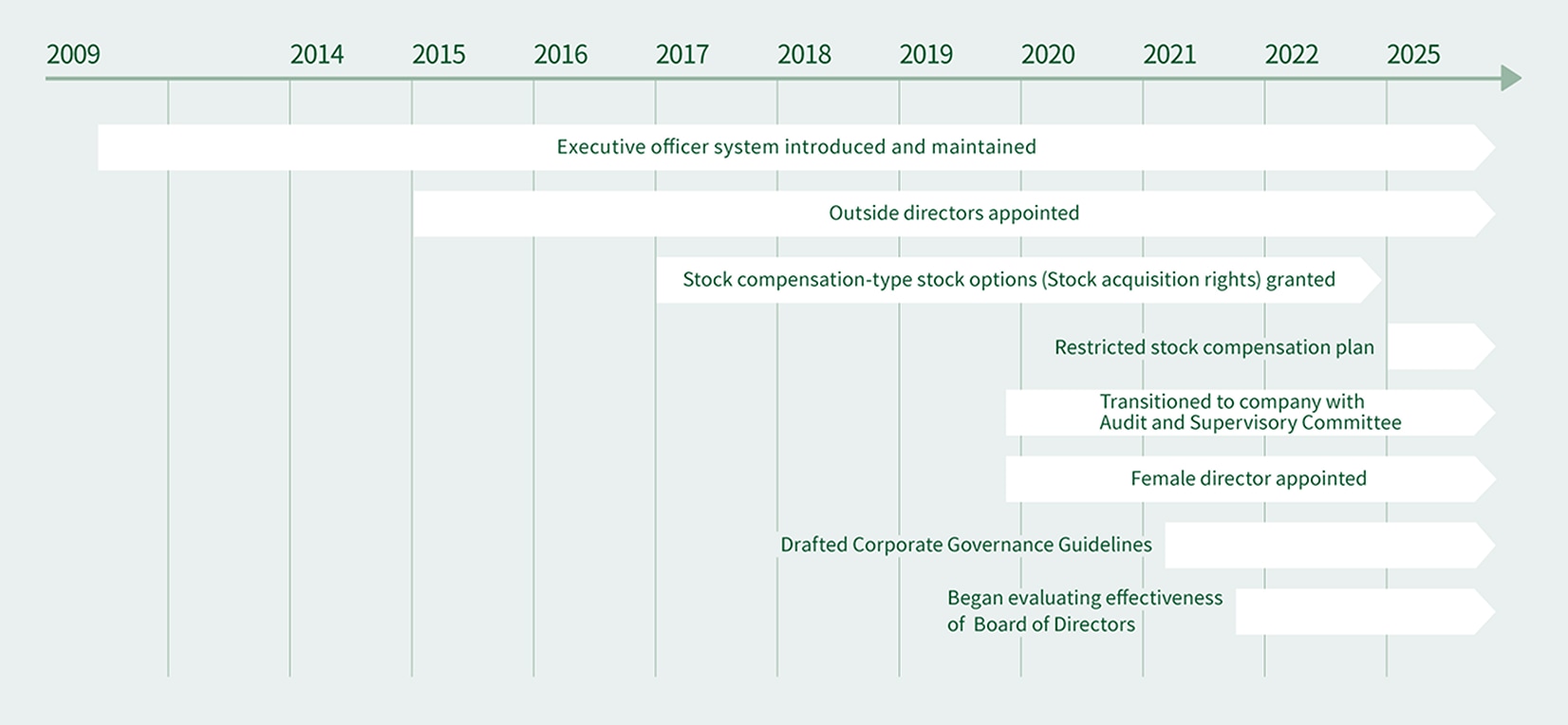
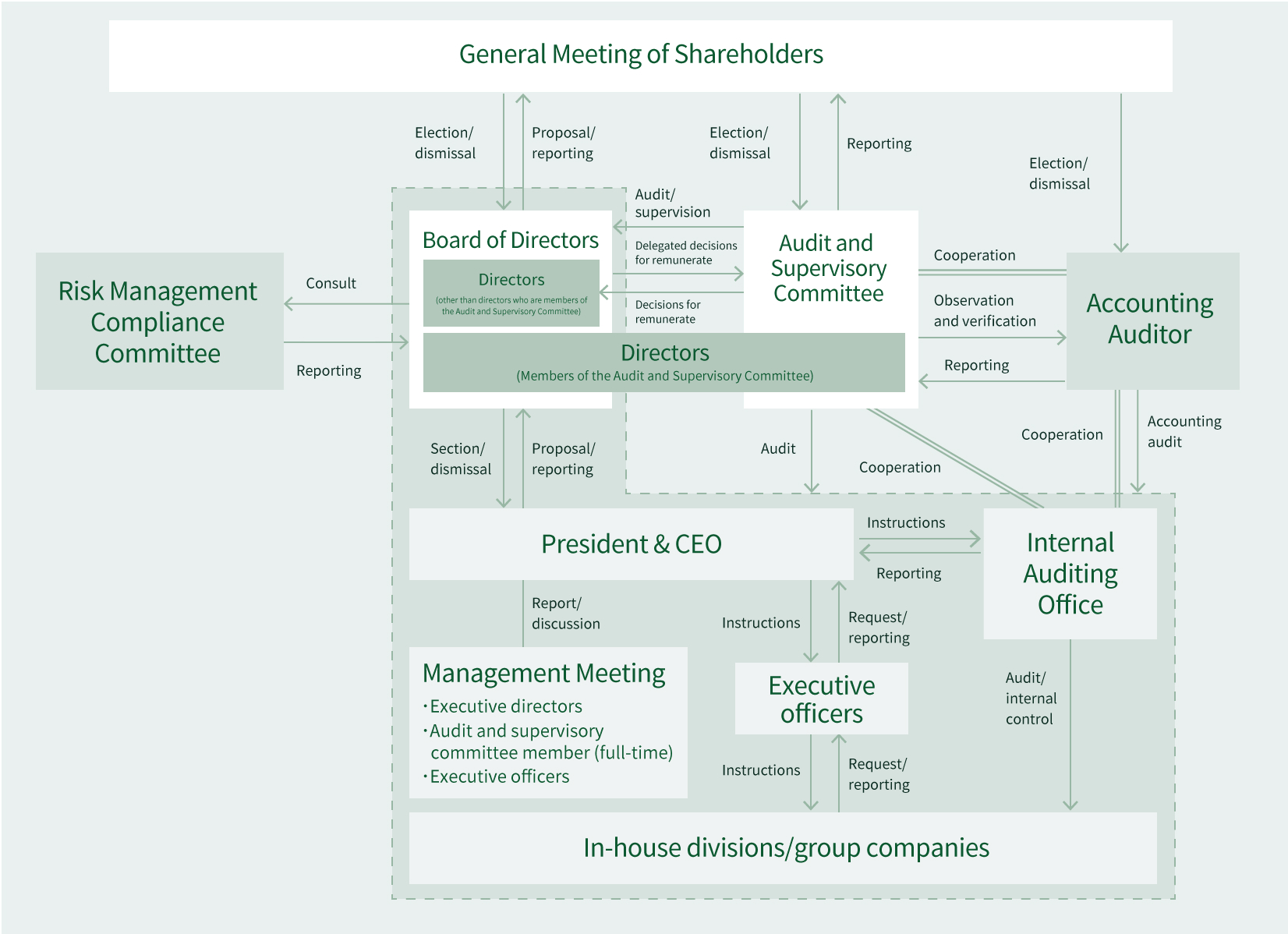
The Board of Directors comprises seven members. In principle, the Board of Directors meets regularly once a month and holds special meetings as necessary. The Board of Directors discusses and decides on basic business policy, important matters related to business, such as business strategies, as well as issues set forth by law in addition to hearing reports on important matters and supervising the status of business executed by directors. Note that in line with provisions in the Articles of Incorporation and decisions by the Board of Directors, FGI delegates the execution of important business to directors, but not directors who are members of the Audit and Supervisory Committee, with the exception of such business issues as matters subject to approval by the Board of Directors by law, investments and loans above a certain limit, and organizational changes. Go to “Executives Members”for a list of the members on the Board of Directors.
The Audit and Supervisory Committee comprises three members, and all members of this committee are outside directors. In line with auditing standards set by the Audit and Supervisory Committee as well as auditing plans, members of the committee audit and supervise the execution of duties by directors through attendance at important meetings, such as those of the Board of Directors, as well as attendance by the full-time member at the Management Meeting and by exercising the right to express opinions at the general meeting of shareholders on the appointment and dismissal of and remuneration for directors. In addition, the Audit and Supervisory Committee discusses remuneration proposals for each director and has final say, based on a draft prepared by the President who evaluates each director.
FGI separated the management decision-making and supervisory function from the business execution function and introduced an executive officer system to expedite decision-making and strengthen the business execution structure. Currently, the Company has nine executive officers, three of whom also services as a director.
The Management Meeting has the participation of directors with responsibility for executing business, the director who is a full-time member of the Audit and Supervisory Committee, executive officers and, as required, the managers of operating divisions and directors at subsidiaries. This is a venue where management hears reports on the status of each business activity and discusses concrete measures for the future.
Composition of remuneration and decision-making process
The remuneration, etc. for Directors shall be composed of the basic remuneration, which is a fixed remuneration, and the restricted share remuneration.
1)Basic remuneration
Basic remuneration for Directors shall be fixed monthly amount that takes a comprehensive view encompassing such factors as position, responsibilities, achievements, contribution to overall business results in the previous fiscal year and responsibility for execution of business activities.
2)Restricted shares remuneration
Non-monetary remuneration, etc. shall be allocated as restricted shares remuneration, and in principle, once each fiscal year, after taking into consideration the purpose of the restricted share remuneration plan, the position and scope of responsibilities of each eligible Director, and other various circumstances, with the aim of providing Directors with incentives to further increase their motivation and morale to contribute to the increase of share price and the sustained improvement of corporate value, and to further share the value with the Company’s shareholders. The number of shares or the amount of monetary remuneration claim to be allotted to each eligible Director shall be within the scope resolved at the general meeting of shareholders of the Company and shall be calculated by taking into consideration not to exceed 20% of the total amount of dividends for the immediately preceding fiscal year. In addition, the restricted shares to be granted [shall be treasury shares, and may not be transferred, mortgaged, or otherwise disposed of from the delivery date of such restricted shares to the date of resignation or retirement from the position of directors of the Company or other positions determined by the Board of Directors of the Company.
In the event of any of the following cases, such remuneration, etc., shall not be paid:
(1) a case where there is no distributable amount as set forth in Article 461 of the Companies Act at the end of the immediately preceding fiscal year;
(2) a case where the Company does not hold treasury shares for the granting;
(3) a case where there is a loss relating to the net profit or loss for the year attributable to the shareholders of the parent company in the previous year’s consolidated profit and loss statement; or
(4) a case where there is a loss relating to the ordinary profit and loss in the previous year’s consolidated profit and loss statement.
The decision on the amount of remuneration for each individual Director shall be delegated to the Audit and Supervisory Committee, which is composed of independent outside directors, by a resolution of the Board of Directors. The Audit and Supervisory Committee shall deliberate and make the final decision on the remuneration proposals for each Director based on the draft formulated by the President and CEO after evaluating each Director in accordance with the policies described in 1) above for basic remuneration and 2) above for non-monetary remuneration.
Remuneration for directors who are members of the Audit and Supervisory Committee comprises only basic remuneration from the perspective of the role that each director on the committee plays, and is determined through discussions among directors of the same committee, taking into account such factors as whether the director is full-time or part-time and the division of work.

Beginning in fiscal 2021, FGI analyzes and evaluates the effectiveness of its Board of Directors. The results of evaluation are available for viewing by following the link provided below. From the perspective of improving the effectiveness of the Board of Directors, efforts are ongoing to run meeting more efficiently and to explore discussion topics more deeply.
Overview of evaluation results on effectiveness of Board of Directors
FGI established and enforces risk management rules, basic policy for risk management, and rules for contingency planning to control risks. Divisions are assigned risk categories and undertake measures to control respective risk, enabling the Company to realize a broad-based corporate risk management system. To reinforce the corporate legal risk management structure for business management and day-to-day operations, the Company retains the services of a law firm for legal guidance, including fact-based opinions and advice. The Company and its subsidiaries obtain legal assistance for each structured finance transaction and asset management services at the time of arrangement or undertaking, and put pertinent documentation through a legal check.
To facilitate internal audits, FGI established the Internal Audit Office, staffed by one person in concurrent roles, under the direct supervision of the president. This office audits the operations of the Company and principal subsidiaries, with audits primarily intended to identify the risks inherent in each operating division and to promote improvement in operations to minimize risk while building a better legal compliance structure. The results of such audits are forwarded to the president as well as the Audit and Supervisory Committee and relevant divisions, with follow-up on any corrective measures implemented to address problems found. In addition, the Internal Audit Office reports to the Board of Directors and the Audit and Supervisory Committee on important matters, such as internal audit plans and the results of internal audits. FGI has assigned two people to deal with the internal control reporting system, based on the Financial Instruments and Exchange Law, and assesses companywide controls and the design and implementation of business processes, in compliance with “Standards for Management Assessment and Audit Concerning Internal Control Over Financial Reporting.” The results of internal control assessment are reported to the president, the Board of Directors and the Audit and Supervisory Committee in a timely fashion. The Audit and Supervisory Committee comprises three members, all of whom are outside directors. Each director who is a member of this committee audits the execution of duties by directors, except those who are members of this committee, according to audit policy and audit plans determined by the Audit and Supervisory Committee. Note that Atsuhiko Nozaki has experience in the audit department and as a corporate auditor at life insurance company. Kenjiro Suzuki has held key senior positions in financial administration as well as the financial sector. Toru Ohyama is active in the public underwriting department of a securities company and as a stock consultant. Each of these outside directors brings considerable insights related to their area of financial and accounting expertise.
The Audit and Supervisory Committee maintains close contact with the Internal Audit Office during the execution of audits to pinpoint the status of corporate activities and finances and in the execution of other auditing duties. The committee receives reports on audits undertaken by the Internal Audit Office. FGI has engaged Ernst & Young ShinNihon LLC to provide accounting auditor services and entrusts this firm to execute audits in accordance with such laws as the Companies Act. SGI-Group B.V, an overseas subsidiary, entrusts audit certification work to a member firm of Ernst & Young, which falls under the same network as Ernst & Young ShinNihon. The Audit and Supervisory Committee and the Internal Auditing Office actively exchange opinions and information, including quarterly reports from the accounting auditor, and seek to improve the quality of audits. In addition, Key Audit Matters (KAM) are discussed by the Audit and Supervisory Committee and the accounting auditor from an auditing perspective. Meanwhile, the Accounting Department confirms with the accounting auditor ahead of each audit that accounting treatment is appropriate to the respective audit and that the audit properly adheres to established accounting standards.